Fast facts on serotonin
Here are some key points about serotonin. More detail and supporting information is in the main article.
- Serotonin is a chemical created by the human body. It works as a neurotransmitter.
- It is commonly regarded as a chemical that is responsible for maintaining mood balance.
- Serotonin is created by a biochemical conversion process.
- Serotonin is manufactured in the brain and the intestines. The majority of the body's serotonin, between 80-90%, can be found in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Serotonin that is used inside the brain must be produced within it.
- It is thought that serotonin can affect mood and social behavior, appetite and digestion, sleep, memory and sexual desire and function.
- An association has been made between depression and serotonin. Scientists remain unsure whether decreased levels of serotonin contribute to depression or depression causes a decrease in serotonin levels.
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can affect the levels of serotonin in the body.
- If excessive amounts of serotonin are accumulated within the body then serotonin syndrome can occur.
- Other ways to increase body serotonin levels include mood induction, light, exercise and diet.
What is serotonin?2
Serotonin is created by a biochemical conversion process which combines tryptophan, a component of proteins, with tryptophan hydroxylase, a chemical reactor. Together, they form 5-hydroxyltryptamine (5-HT), also referred to as serotonin.
Serotonin is most commonly believed to be a neurotransmitter, although some consider the chemical to be a hormone.
Where does serotonin come from?2,3
Serotonin is manufactured in the brain and the intestines. The majority of the body's serotonin, between 80-90%, can be found in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It can also be found in the blood platelets and the central nervous system (CNS).
As serotonin can be found widely across the body, it is believed that the chemical plays a role in influencing a variety of body and psychological functions.
Serotonin cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, therefore, serotonin that is used inside the brain must be produced within it.
What does serotonin do?2,3
As a neurotransmitter, serotonin relays signals between nerve cells (neurons), regulating their intensity.
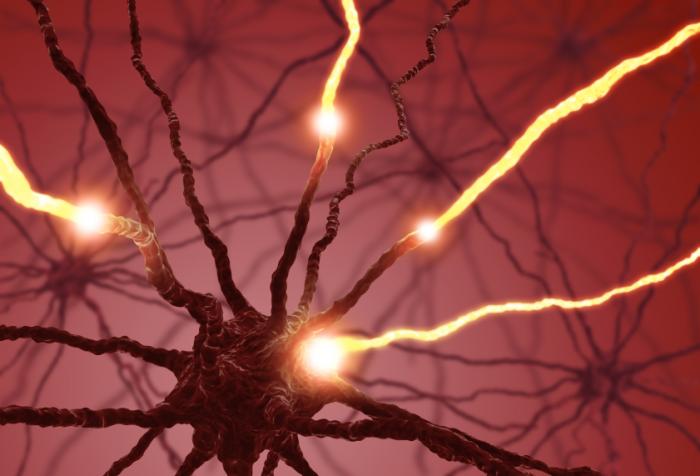
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter, regulating signals between neurons.
Serotonin is widely believed to play a key role in the central nervous system, as well as in the general functioning of the body and in particular the GI tract. Studies have found links between serotonin and bone metabolism, breast milk production, liver regeneration and cell division.
As a neurotransmitter, serotonin influences both directly and indirectly the majority of brain cells. The following is a list of things that it is thought that serotonin could affect:
- Mood and social behavior
- Appetite and digestion
- Sleep
- Memory
- Sexual desire and function.
The link between serotonin and depression24
It is unknown precisely what causes depression. It is thought to be likely that an imbalance of neurotransmitters or hormones in the body can lead to the disorder.

Serotonin levels are heavily associated with depression.
An association has been made between depression and serotonin, although scientists are unsure whether decreased levels of serotonin contribute to depression or depression causes a decrease in serotonin levels.
Although it is possible to measure the level of serotonin in the bloodstream, via a serum serotonin level test, it is currently not possible to measure serotonin levels within the brain. Researchers do not know whether serotonin levels in the bloodstream reflect the serotonin levels in the brain.
It is believed that medication such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) that can affect the levels of serotonin in the body work as antidepressants and are able to relieve the symptoms of depression. It is unknown precisely how they work, however.
A recent study may offer evidence contrary to these widely-held theories. Scientists ran mice without the capacity to create serotonin through a series of behavioral tests.The mice did not show any signs of depression, suggesting that factors other than serotonin could be involved with the development of depression.12
SSRIs and serotonin levels4
SSRIs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat depression and are the most commonly prescribed antidepressants. Common examples of SSRIs are citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine and sertraline.
Normally once a neurotransmitter has transmitted its neural impulse it is generally reabsorbed. SSRIs inhibit the re-absorption of serotonin and thus serotonin levels in the body increase. It is believed that changing the balance of serotonin in the body helps brain cells send and receive messages, and in turn this boosts overall mood.
Recreational drugs such as MDMA and cocaine also inhibit the re-absorption of serotonin in order to create their highs.
SSRIs can sometimes cause side effects. They all have different chemical compositions, and so one may affect someone differently than others. Side effects may include the following:
- Agitation
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Dry mouth
- Headaches
- Insomnia
- Nausea or vomiting
- Reduced libido
- Weight gain or loss.
from MNT knowledge center
No comments:
Post a Comment